A problem in the Chinese version of GPT-4o can lead to poor performance and erroneous responses.
On May 13, OpenAI unveiled its latest artificial intelligence model, GPT-4o (Omni). However, a few days after the release of the model, Chinese users noticed that something went wrong in the new version: the tokens used to parse the text contained a lot of spam and pornographic phrases.
On May 14, Tianle Cai, a graduate student at Princeton University who studies inference efficiency in large language models, gained access to the public token library and compiled a list of the 100 longest Chinese-language tokens used by the model to process Chinese queries.
It turned out that only 3 of them were common enough to be used in everyday conversations; the rest were words and expressions related to gambling and pornography. The longest token was 10.5 Chinese characters long and literally meant "free Japanese pornographic videos to watch".
OpenAI did not comment on the situation.
GPT-4o was supposed to surpass its predecessors in handling multilingual tasks thanks to a new tokenization tool that compresses texts in non-English languages better. However, for the Chinese language, the new tokenization has resulted in a large number of meaningless phrases. Experts attribute this to insufficient data cleaning before training the model.
Incorrect tokens make it difficult for the model to understand their meaning, which can lead to the generation of erroneous or insecure responses, which allows researchers to bypass OpenAI's security measures.
Models are easiest to process text character-by-character, but this requires more time and resources. Tokens, which are sequences of characters with a specific value, allow the model to work faster and more efficiently. With the release of GPT-4o, OpenAI introduced a new tokenizer that added support for non-English languages. In total, the new tokenizer has 200,000 tokens, about 24% of which are in other languages, including Russian, Arabic and Vietnamese.
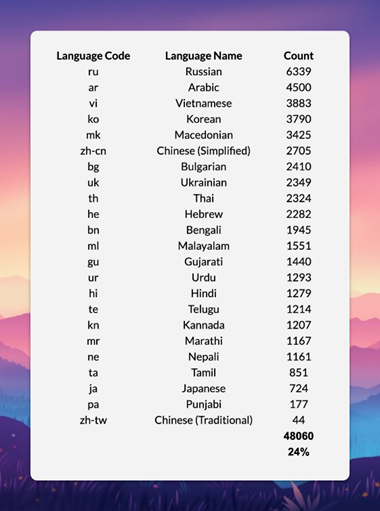
AI investor Didi Das believes that the main advantage of the new tokenizer is to reduce the cost of processing requests in these languages, and not to improve the quality. Das also noted that tokens in Hindi and Bengali reflect people's discussions, including names and titles, without spam and pornographic expressions, unlike Chinese tokens.
The difference is due to the quality of training data: Chinese tokens contain a lot of spam words used in the context of pornography and gambling. This indicates that the Chinese language data corpus was contaminated and not properly cleaned.
Such contaminated data may be the result of practices where spam sites embed their ads in the content of other sites to bypass filters and be indexed by search engines, as confirmed by Chinese users who report frequent occurrence of spam sites in Google search results.
Das claims that the solution to the spam problem is simple and can include simple filtering methods. However, OpenAI, according to Das, did not properly clean up the data for the Chinese language before the release of GPT-4o. It is worth noting that such problems were absent in previous versions – GPT-3.5 and GPT-4.
Users also discovered that tokens can be used to bypass the model's security mechanisms, forcing it to generate forbidden responses. For example, a request to translate long Chinese tokens may result in words that are not included in the request, which is a sign of the model's" hallucinations".
The problem occurs when the tokenizer and the language model itself are trained on different data sets. Because of this, the model does not understand rarely used tokens, which can cause strange and unsafe responses.
The solution is to make the data set for the tokenizer match the data set for the model to avoid discrepancies. However, this is difficult to implement in practice, as learning language models takes months and requires constant improvement and data filtering.
Experts believe that the problem is not difficult to solve, but it can become more complex with the development of the model, especially in multimodal systems that include text and visual elements. If the problem with Chinese tokens is not resolved, it can get worse when working with visual tokens, which requires even more complex data filtering.
On May 13, OpenAI unveiled its latest artificial intelligence model, GPT-4o (Omni). However, a few days after the release of the model, Chinese users noticed that something went wrong in the new version: the tokens used to parse the text contained a lot of spam and pornographic phrases.
On May 14, Tianle Cai, a graduate student at Princeton University who studies inference efficiency in large language models, gained access to the public token library and compiled a list of the 100 longest Chinese-language tokens used by the model to process Chinese queries.
It turned out that only 3 of them were common enough to be used in everyday conversations; the rest were words and expressions related to gambling and pornography. The longest token was 10.5 Chinese characters long and literally meant "free Japanese pornographic videos to watch".
OpenAI did not comment on the situation.
GPT-4o was supposed to surpass its predecessors in handling multilingual tasks thanks to a new tokenization tool that compresses texts in non-English languages better. However, for the Chinese language, the new tokenization has resulted in a large number of meaningless phrases. Experts attribute this to insufficient data cleaning before training the model.
Incorrect tokens make it difficult for the model to understand their meaning, which can lead to the generation of erroneous or insecure responses, which allows researchers to bypass OpenAI's security measures.
Models are easiest to process text character-by-character, but this requires more time and resources. Tokens, which are sequences of characters with a specific value, allow the model to work faster and more efficiently. With the release of GPT-4o, OpenAI introduced a new tokenizer that added support for non-English languages. In total, the new tokenizer has 200,000 tokens, about 24% of which are in other languages, including Russian, Arabic and Vietnamese.

AI investor Didi Das believes that the main advantage of the new tokenizer is to reduce the cost of processing requests in these languages, and not to improve the quality. Das also noted that tokens in Hindi and Bengali reflect people's discussions, including names and titles, without spam and pornographic expressions, unlike Chinese tokens.
The difference is due to the quality of training data: Chinese tokens contain a lot of spam words used in the context of pornography and gambling. This indicates that the Chinese language data corpus was contaminated and not properly cleaned.
Such contaminated data may be the result of practices where spam sites embed their ads in the content of other sites to bypass filters and be indexed by search engines, as confirmed by Chinese users who report frequent occurrence of spam sites in Google search results.
Das claims that the solution to the spam problem is simple and can include simple filtering methods. However, OpenAI, according to Das, did not properly clean up the data for the Chinese language before the release of GPT-4o. It is worth noting that such problems were absent in previous versions – GPT-3.5 and GPT-4.
Users also discovered that tokens can be used to bypass the model's security mechanisms, forcing it to generate forbidden responses. For example, a request to translate long Chinese tokens may result in words that are not included in the request, which is a sign of the model's" hallucinations".
The problem occurs when the tokenizer and the language model itself are trained on different data sets. Because of this, the model does not understand rarely used tokens, which can cause strange and unsafe responses.
The solution is to make the data set for the tokenizer match the data set for the model to avoid discrepancies. However, this is difficult to implement in practice, as learning language models takes months and requires constant improvement and data filtering.
Experts believe that the problem is not difficult to solve, but it can become more complex with the development of the model, especially in multimodal systems that include text and visual elements. If the problem with Chinese tokens is not resolved, it can get worse when working with visual tokens, which requires even more complex data filtering.
