The new technique allows you to reveal the real address of the server on the darknet.
Tor's hidden services provide anonymity for web services that are resistant to identification and tracking. But a recent discovery revealed a new way to expose the real IP address of these services using an HTTP header known as an Etag.
Etag – a unique identifier created by the server when a resource is requested by the client. The latter uses it to determine whether the resource version is up-to-date. If the Etag is not changed, the client switches to the cached version, saving traffic and speeding up downloads.
But an Etag can also serve as a tracking tool. It can contain information about the server, including the IP address, time, or hash. This means that when requesting the same resource from different hidden Tor services that belong to the same server, the client can get the same Etag that reveals the real IP address of the server.
An article on Medium demonstrated how the author, using the curl and torsocks tools and Etag comparison, was able to reveal the IP address of the anonymous Tor service belonging to the RagnarLocker ransomware. All Etags were identical and contained a hash of the server's IP address, which allowed us to determine its real address and location.
According to a study, a well-known ransomware group Ragnar Locker attacked the video game company Capcom , claiming to have stolen one terabyte of data. Capcom refused Ragnar Locker's demands, and 67 GB of stolen files were published on the Dark Web.

The leak site contained only the link, not the files themselves. Instead, a special Onion address was provided to store files such as leaked data, which was apparently prepared by the Ragnar Locker operator. The files were split into several parts and placed at an Onion address starting with t2w....
Usually, when searching for the source IP address of a site in the Dark Web, the site source code, SSL certificate, response headers, etc. are checked to get unique strings and fingerprint information, and then scanning services such as Shodan, Censys, and others search for the IP address. In this study, the response headers were checked. If the response header contains a unique string, you can get the source IP address.
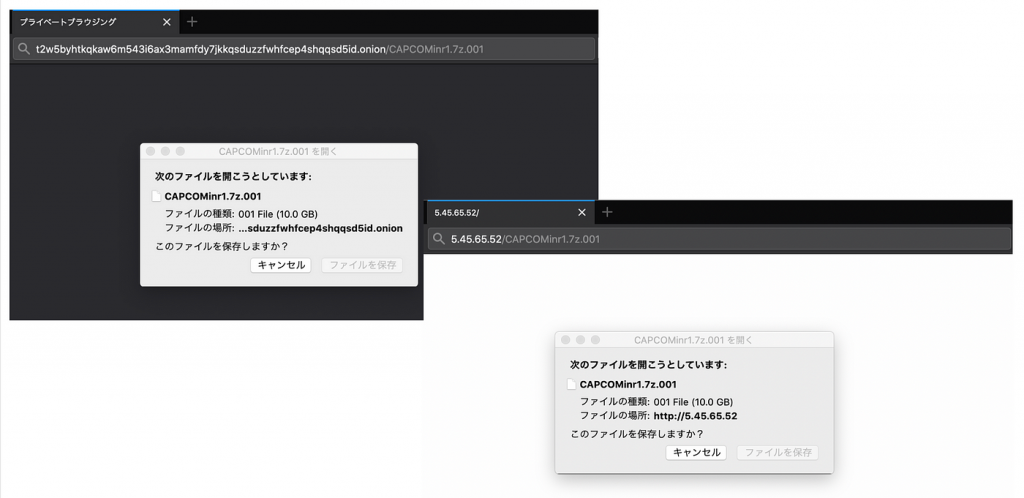
After checking the response headers and detecting the same ETag, the researcher tried uploading a file with the same name on the Onion address and on the IP address, and confirmed that the file with the same name was located as shown in the image below. So we can say that the source IP of the Onion address t2w5by.... onion is 5.45.65.52.
Later, the IP address 5.45.65.52 was mentioned in the FBI's operational report . The report says that the address was used as a server for hosting compromised Capcom data.
This method can be used both by attackers to deanonymize users and providers of hidden Tor services, and by law enforcement agencies in the fight against illegal activity. However, there are ways to protect yourself, such as disabling Etag on the server or using a proxy to change the Etag during transmission.
(c) https://www.securitylab.ru/news/539103.php
Tor's hidden services provide anonymity for web services that are resistant to identification and tracking. But a recent discovery revealed a new way to expose the real IP address of these services using an HTTP header known as an Etag.
Etag – a unique identifier created by the server when a resource is requested by the client. The latter uses it to determine whether the resource version is up-to-date. If the Etag is not changed, the client switches to the cached version, saving traffic and speeding up downloads.
But an Etag can also serve as a tracking tool. It can contain information about the server, including the IP address, time, or hash. This means that when requesting the same resource from different hidden Tor services that belong to the same server, the client can get the same Etag that reveals the real IP address of the server.
An article on Medium demonstrated how the author, using the curl and torsocks tools and Etag comparison, was able to reveal the IP address of the anonymous Tor service belonging to the RagnarLocker ransomware. All Etags were identical and contained a hash of the server's IP address, which allowed us to determine its real address and location.
According to a study, a well-known ransomware group Ragnar Locker attacked the video game company Capcom , claiming to have stolen one terabyte of data. Capcom refused Ragnar Locker's demands, and 67 GB of stolen files were published on the Dark Web.

The leak site contained only the link, not the files themselves. Instead, a special Onion address was provided to store files such as leaked data, which was apparently prepared by the Ragnar Locker operator. The files were split into several parts and placed at an Onion address starting with t2w....
Usually, when searching for the source IP address of a site in the Dark Web, the site source code, SSL certificate, response headers, etc. are checked to get unique strings and fingerprint information, and then scanning services such as Shodan, Censys, and others search for the IP address. In this study, the response headers were checked. If the response header contains a unique string, you can get the source IP address.
After checking the response headers and detecting the same ETag, the researcher tried uploading a file with the same name on the Onion address and on the IP address, and confirmed that the file with the same name was located as shown in the image below. So we can say that the source IP of the Onion address t2w5by.... onion is 5.45.65.52.

Later, the IP address 5.45.65.52 was mentioned in the FBI's operational report . The report says that the address was used as a server for hosting compromised Capcom data.
This method can be used both by attackers to deanonymize users and providers of hidden Tor services, and by law enforcement agencies in the fight against illegal activity. However, there are ways to protect yourself, such as disabling Etag on the server or using a proxy to change the Etag during transmission.
(c) https://www.securitylab.ru/news/539103.php
