Why is the video platform buried in fraudulent videos, and naive users go along with hackers?
Recently, Fortinet experts discovered a new cyber threat: attackers use YouTube videos associated with pirated software to distribute a data thief called Lumma.
These videos usually contain information about hacked apps, provide similar installation instructions, and contain malicious URLs, often shortened using services like TinyURL and Cuttly to lull a potential victim's guard down.
Similar methods have long been used to spread various types of malware, including malware designed to steal data, cryptocurrencies, and illegal cryptomining.
It is noteworthy that such blatantly fraudulent videos can hang on the popular video platform for a very long time before they are finally removed. And you shouldn't even talk about numerous reallocations.
Whether Google is to blame for how it implemented the moderation system for content uploaded to YouTube remains a mystery. However, the problem can hardly be solved with the help of modern technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
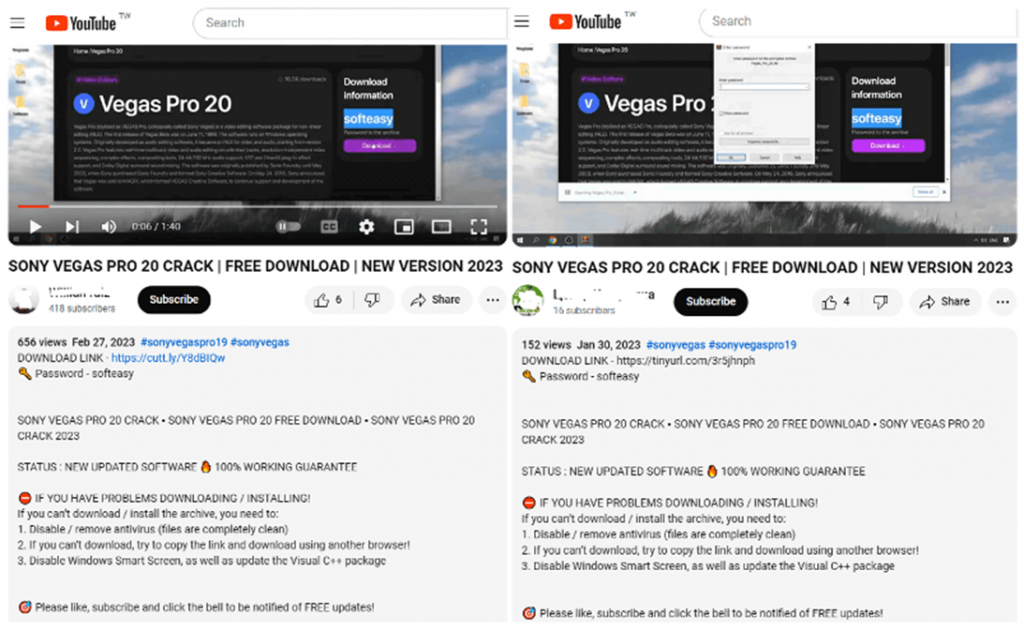
In the latest recorded attack, attackers targeted users who search YouTube for hacked versions of legitimate video editors, such as Vegas Pro. In phishing videos, hackers use social engineering techniques that encourage the viewer to click on a link in the video description, which leads to downloading a fake program installer from the MediaFire file sharing site.
The installer, in turn, contains a malicious LNK file disguised as an executable installation file, which is secretly loaded by the boot loader .NET from the GitHub repository. After that, as well as checking whether the malware is running on the VM, Lumma Stealer starts its work on the compromised system.
The Lumma infostealer, written in C and sold on underground forums from the end of 2022, is capable of collecting and transmitting confidential data to a server controlled by attackers. According to some reports, the malware was first detected in real attacks back in 2018.
In October 2023, we talked about the spread of this insidious malware through Discord-bots that exploit the API of the popular platform for gamers.
For effective protection against infostealers such as Lumma and other cyber threats, you should think twice before launching applications downloaded from dubious sources. It is best to use only official channels for downloading any software, and also get a reliable antivirus solution to further improve your security.
Recently, Fortinet experts discovered a new cyber threat: attackers use YouTube videos associated with pirated software to distribute a data thief called Lumma.
These videos usually contain information about hacked apps, provide similar installation instructions, and contain malicious URLs, often shortened using services like TinyURL and Cuttly to lull a potential victim's guard down.
Similar methods have long been used to spread various types of malware, including malware designed to steal data, cryptocurrencies, and illegal cryptomining.
It is noteworthy that such blatantly fraudulent videos can hang on the popular video platform for a very long time before they are finally removed. And you shouldn't even talk about numerous reallocations.
Whether Google is to blame for how it implemented the moderation system for content uploaded to YouTube remains a mystery. However, the problem can hardly be solved with the help of modern technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
In the latest recorded attack, attackers targeted users who search YouTube for hacked versions of legitimate video editors, such as Vegas Pro. In phishing videos, hackers use social engineering techniques that encourage the viewer to click on a link in the video description, which leads to downloading a fake program installer from the MediaFire file sharing site.

The installer, in turn, contains a malicious LNK file disguised as an executable installation file, which is secretly loaded by the boot loader .NET from the GitHub repository. After that, as well as checking whether the malware is running on the VM, Lumma Stealer starts its work on the compromised system.
The Lumma infostealer, written in C and sold on underground forums from the end of 2022, is capable of collecting and transmitting confidential data to a server controlled by attackers. According to some reports, the malware was first detected in real attacks back in 2018.
In October 2023, we talked about the spread of this insidious malware through Discord-bots that exploit the API of the popular platform for gamers.
For effective protection against infostealers such as Lumma and other cyber threats, you should think twice before launching applications downloaded from dubious sources. It is best to use only official channels for downloading any software, and also get a reliable antivirus solution to further improve your security.
