Carding 4 Carders
Professional
- Messages
- 2,724
- Reaction score
- 1,584
- Points
- 113
In this article, I will talk about how resource administrators are calculated in the Tor Network, that is, in the Dark Web. We will look at the structure of sites in Tor, discuss the known cases of deanon and many other features of this dark corner of the Internet, which is considered anonymous. Along the way, I'll recommend programs that will help you get started.
I think you already know that sites with addresses ending in .onion, — they are not simple and you won't be able to open them in a normal browser without additional effort. The so-called dark web consists of such sites. Very often they are dedicated to the trade in illegal goods and services. Of course, because the administrators of these sites do not have to fill in their contact details when registering, there is no censorship, and "onion" routing through a series of proxy servers should ensure anonymity.
Sites on the Tor Network are not indexed by regular search engines, but there are specialized search engines that search only in Tor. In general, as you understand, this is a whole separate world.
Perfect protection from surveillance? Not quite. In theory, anyone can make their computer a proxy node and collect data about requests. You may ask, who needs it if the information is encrypted? What if an attacker collects some of the information before encryption, infecting the input node? Or vice versa-output, and get data about the requested resources? It is the second option that is most common.
In addition, an attacker can modify or completely change the information transmitted from the server to the client. This way, you can even infect the client's device with malicious code.
In 2020, the hacker group KAX17 was discovered, which managed 900 infected servers, which were accessed by up to 16% of Tor users.
Here are some tools that help you explore Tor nodes::
That is why experts advise not to enable JavaScript on sites on the darknet, or at least not to use the browser in full-screen mode, so as not to give out the screen size. A digital fingerprint is certainly not as scary as real personal data, but it allows you to select a unique user from a certain number.
Есть research that showed that DNS traffic on the Tor network can be used to accurately determine the sites visited. Researchers used various methods to analyze DNS queries passing through Tor exit nodes and find out the correlations of these queries with specific sites.
You can simply search for domains in queries. Because in the addresses .onion domains consist of generated identifiers, and they can be easily compared with identifiers in DNS queries and set up matches. This allows you to determine which specific sites the user visited through Tor.
In rare cases, administrators do not delete metadata from files hosted on the site, and metadata may include information such as the camera model, name, geolocation, and more. Now even regular social networks delete metadata when uploading files.
Imagine: a client buys a crypt, buys something with it on the darknet, the cryptocurrency is stored on the marketplace deposit, then most of it goes to the seller, and then he tries to exchange it for fiat currency.
It turns out that you can determine which exchange the seller uses, if you know the address of his cryptocurrency wallet. To do this, it is enough to visualize its activity using a special program. On the wallet of the exchanger, of course, there will be a huge number of transactions and a considerable amount of money.
Visualizers are often paid, but there are also several free ones:
Cryptocurrency mixers are often used in money laundering. They allow you to hide cryptocurrency assets, distribute them to many other wallets, and then transfer them back to one. This makes it harder to track transactions, but it doesn't make them completely anonymous.
If you visualize the transactions of the wallet that the mixer used, you will notice the following features:
As you understand, money laundering and its tracking is a separate big topic. But you need to know about it, at least at a basic level. There are a huge number of schemes for legalizing funds obtained by criminal means-from the creation of offshore organizations to the purchase of various properties. Of course, we will not discuss all this here.
Here are the search engines available in clearance and indexing onion sites:
Many of them are convenient and allow you to combine results from the clearnet and darkweb.
Here is a list of search engines that have sites on the Tor network (links are given to onion addresses):
With these systems, you can try basic tricks like finding an exact match (double quotes), specifying the site where to search (operatorsite), operator intext, and others in the same spirit. In most search engines, this will work.
If our goal is to find out the forum administrator, then any intelligence techniques are used. For example, if you know their interests, then you can go through the thematic forums in search of mentions of their nickname.
Here is an example of a query that will return a search result for the archive of the Hacker forum in search of the moon user:
By the way, about thematic forums. There are wikis that collect links to sites in the dark Web, and from there it is easy to get a selection of addresses of criminal forums. Here are some of them::
They're human, too!
Forum users and marketplace administrators aren't robots either, so they tend to make mistakes. For example, someone can send a photo of themselves to someone they met online. I personally heard about several cases when administrators of the largest illegal sites were detained, offering to meet. Experts use a variety of traps and honeypots to slip the criminal a file, a link, and sometimes an entire fake app or marketplace.
As for IP Logger, I don't recommend using it when trying to track down professionals. This program is more like a child's toy, rather than a working tool, and a more or less advanced user will immediately suspect something bad.
For an example, let's look at the site AmIUnique.org. The service will easily detect the engine version, OS, language, fonts, plugins, and with some accuracy — the audio and video plugins supported by the browser. It's hard to call this an accurate identification, but identifying one suspect out of a thousand might help.
Tor Browser specially masks the screen resolution to make identification more difficult, plus users can replace the fingerprint themselves based on the canvas tag. All this makes fingerprinting less accurate, but it doesn't prevent it completely.
There are also more sophisticated tactics based on fingerprinting. Not everyone knows that if you open Tor Browser and normal and then switch between them with hot keys or the mouse, you can get a link between your real IP and the IP in the Tor network. They bring up unique patterns like the position of the mouse cursor, which can be tracked. The same goes for using two tabs in Tor Browser. Tor will use different input nodes for them, but if JavaScript is enabled, the relationship between tabs can still be established.

All these little features will help you find other accounts on other forums, social networks, and so on. It is said that such mistakes were made by Ross Ulbricht, the owner of a large marketplace Silk Road.
Let's start with crawlers. They can be used to collect a certain type of data on a site, such as photos, videos, text, and so on. For example, you want to go through all the photos on your site and find those that contain metadata.
Here are some Onion crawlers:
Scrapers work according to a predefined algorithm that determines what data to collect and how to extract it. They usually make requests to the server, and then analyze the resulting HTML to extract the necessary information. Various methods of parsing pages are used: HTML parsing, search by tags and CSS classes, regular expressions, and so on. Often sites are uploaded in their entirety for further analysis.
Here are some scraping programs and libraries:
Spiders are designed to index hundreds or thousands of links. For Tor, there are Onioff и Onion Spider.

You can use the Regshot program to analyze the registry.
For network traffic analysis, I recommend Wireshark and NetworkMiner. Wireshark is good for detecting different types of packets and establishing connections between nodes. It helps you identify the characteristics of the protocols used in Tor. And NetworkMiner specializes in analyzing network traffic and identifying hidden connections and patterns. NetworkMiner can help you detect and analyze Tor network activity, including sharing information and using anonymous proxy servers.
And of course, you need to study the database of the Tor Browser itself. It is located along this path:
TorBrowser\Browser\TorBrowser\Data\Browser\Profile.default
Here, with certain browser settings, you can store your browsing history, bookmarks, saved passwords, cookies, and other user data.
Studying the data of Bitcoin wallets is a separate and complex topic, but you can use the Internet Evidence Finder to collect evidence.
I think you already know that sites with addresses ending in .onion, — they are not simple and you won't be able to open them in a normal browser without additional effort. The so-called dark web consists of such sites. Very often they are dedicated to the trade in illegal goods and services. Of course, because the administrators of these sites do not have to fill in their contact details when registering, there is no censorship, and "onion" routing through a series of proxy servers should ensure anonymity.
Sites on the Tor Network are not indexed by regular search engines, but there are specialized search engines that search only in Tor. In general, as you understand, this is a whole separate world.
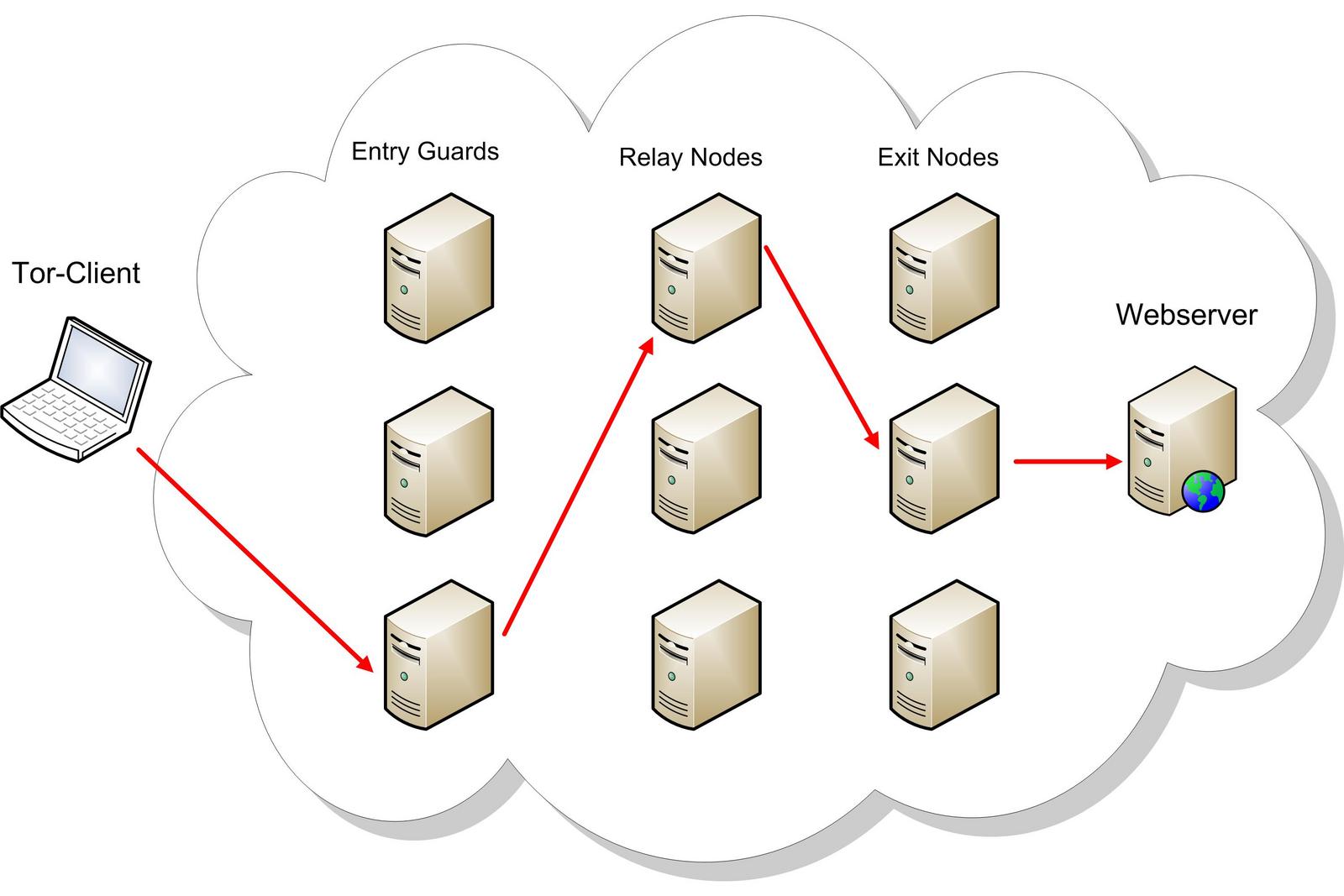
How the Tor Network works
With normal direct IP routing, everything is relatively simple: one node makes a request to some address, the other responds to the same address from which the request was received. In onion routing, any request first passes through three nodes, called Tor nodes. By default, the input and output nodes encrypt information so that it passes through the next node.Perfect protection from surveillance? Not quite. In theory, anyone can make their computer a proxy node and collect data about requests. You may ask, who needs it if the information is encrypted? What if an attacker collects some of the information before encryption, infecting the input node? Or vice versa-output, and get data about the requested resources? It is the second option that is most common.
In addition, an attacker can modify or completely change the information transmitted from the server to the client. This way, you can even infect the client's device with malicious code.
In 2020, the hacker group KAX17 was discovered, which managed 900 infected servers, which were accessed by up to 16% of Tor users.
Here are some tools that help you explore Tor nodes::
- TOR Node List - a list of nodes;
- ExoneraTor - checking the IP address for use as a Tor node;
- Onionite - information about nodes;
- Tor Metrics - information about nodes;
- Collector Tor - archive of host IP and ports.
That is why experts advise not to enable JavaScript on sites on the darknet, or at least not to use the browser in full-screen mode, so as not to give out the screen size. A digital fingerprint is certainly not as scary as real personal data, but it allows you to select a unique user from a certain number.

Onion DNS
Exploration through Whois and DNSdumpster services on the Tor network is simply impossible, because the onion domain system does not work at all like the usual one. Here are its main differences:- There is only a single domain zone .onion, domains consist of generated identifiers, which is why there is basically no hierarchical structure with TLDs, SLDSAND subdomains.
- Decentralized storage is the main problem of the data collector, because it makes it impossible to send a request to Whois. In classical DNS, information about domains and their corresponding IP addresses is stored on centralized DNS servers. In Tor, information about domains .onion and their addresses are stored on distributed nodes in the Tor network.
- The protocols also differ. If classical DNS uses UDP and TCP queries, then the DNS system in Tor directly accesses distributed storage nodes to get the desired address.
www
TorWhois is a kind of Whois service for Tor. Allows you to get information about open ports, certificates, keys, and information about robots.txt.Есть research that showed that DNS traffic on the Tor network can be used to accurately determine the sites visited. Researchers used various methods to analyze DNS queries passing through Tor exit nodes and find out the correlations of these queries with specific sites.
You can simply search for domains in queries. Because in the addresses .onion domains consist of generated identifiers, and they can be easily compared with identifiers in DNS queries and set up matches. This allows you to determine which specific sites the user visited through Tor.
In rare cases, administrators do not delete metadata from files hosted on the site, and metadata may include information such as the camera model, name, geolocation, and more. Now even regular social networks delete metadata when uploading files.
Site structure
Sites in Tor use an ordinary CMS, as well as sites in the "clearnet". Of course, inside all the same HTML, CSS and other familiar technologies. That is, there is nothing surprising or new here. In the screenshot, you can see that the author of the site made it on Bootstrap. And the use of popular technologies, of course, opens up the possibility for automating audit for intelligence purposes. To do this, there are:- Onionscan (onion site audit);
- Onion Nmap (Nmap for the onion site);
- OWASP ZAP (Scanner);
- Nikto (scanner);
- WPScan (scanner);
- Burp Suite (scanner);
- Wapiti (scanner);
- list of vulnerabilities on Mitre.org.

Shadow economy
Most often, darkweb is used for trading prohibited goods and services. The money raised then needs to be withdrawn somehow, and here merchants of prohibited goods invent the most sophisticated schemes. Usually — using cryptocurrency. It is at the stage of withdrawing money that the owners of marketplaces most often come across.Imagine: a client buys a crypt, buys something with it on the darknet, the cryptocurrency is stored on the marketplace deposit, then most of it goes to the seller, and then he tries to exchange it for fiat currency.
It turns out that you can determine which exchange the seller uses, if you know the address of his cryptocurrency wallet. To do this, it is enough to visualize its activity using a special program. On the wallet of the exchanger, of course, there will be a huge number of transactions and a considerable amount of money.
Visualizers are often paid, but there are also several free ones:
Cryptocurrency mixers are often used in money laundering. They allow you to hide cryptocurrency assets, distribute them to many other wallets, and then transfer them back to one. This makes it harder to track transactions, but it doesn't make them completely anonymous.
If you visualize the transactions of the wallet that the mixer used, you will notice the following features:
- multiple inputs and outputs in a single transaction, including addresses that are not associated with the original wallet;
- mixing funds between different addresses and wallets;
- links to other transactions — chains and clusters of transactions associated with the bitcoin mixer;
- heterogeneity of transaction amounts;
- unusual time intervals between transactions.
As you understand, money laundering and its tracking is a separate big topic. But you need to know about it, at least at a basic level. There are a huge number of schemes for legalizing funds obtained by criminal means-from the creation of offshore organizations to the purchase of various properties. Of course, we will not discuss all this here.
Search engines
Search engines and search engines (query recipes) have always been the main weapon of the modern OSINT specialist, and everything is exactly the same on the Tor network. Let's see what search engines are looking for on the dark web.Here are the search engines available in clearance and indexing onion sites:
Many of them are convenient and allow you to combine results from the clearnet and darkweb.
Here is a list of search engines that have sites on the Tor network (links are given to onion addresses):
With these systems, you can try basic tricks like finding an exact match (double quotes), specifying the site where to search (operatorsite), operator intext, and others in the same spirit. In most search engines, this will work.
info
Read more about dorks in the articles "Using little-known Google features to find hidden things" and "Google as a hacking tool. We analyze current recipes of Google Dork Queries".If our goal is to find out the forum administrator, then any intelligence techniques are used. For example, if you know their interests, then you can go through the thematic forums in search of mentions of their nickname.
Here is an example of a query that will return a search result for the archive of the Hacker forum in search of the moon user:
Code:
site:oldforum.xakep.ru intext:moonBy the way, about thematic forums. There are wikis that collect links to sites in the dark Web, and from there it is easy to get a selection of addresses of criminal forums. Here are some of them::
- The Hidden Wiki;
- IACA DarkWeb;
- DarkWeb Links;
- The DarkWeb Links.

They're human, too!
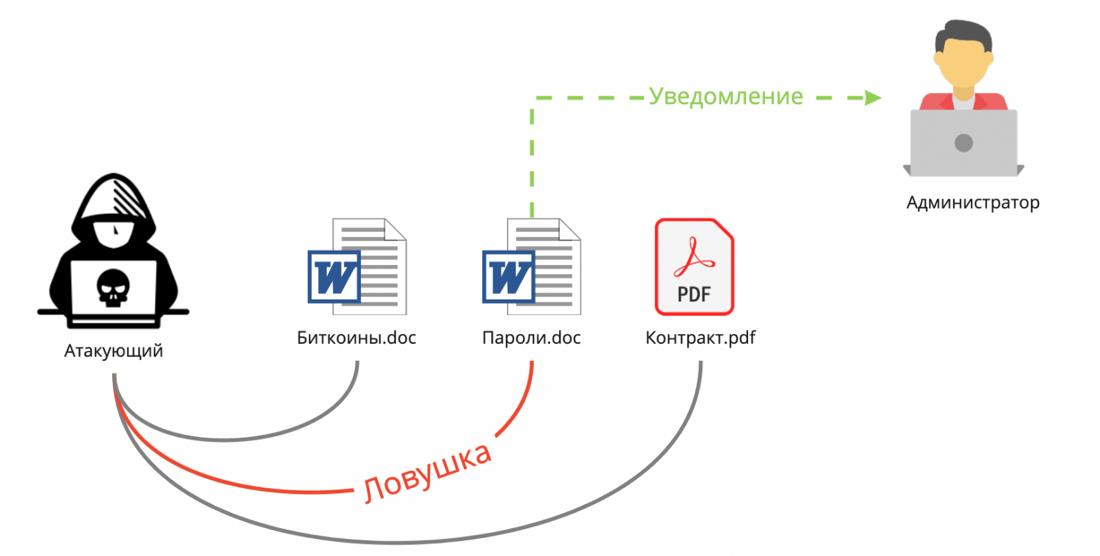
Forum users and marketplace administrators aren't robots either, so they tend to make mistakes. For example, someone can send a photo of themselves to someone they met online. I personally heard about several cases when administrators of the largest illegal sites were detained, offering to meet. Experts use a variety of traps and honeypots to slip the criminal a file, a link, and sometimes an entire fake app or marketplace.
Traps
Traps like IP Logger or Canary Tokens are the simplest and most low — budget things that happen. In the case of Canary Tokens, you can deploy your server using a ready-made Docker image, which was kindly provided to us by the developers. This tool has many interesting features, and, in my opinion, it is often underestimated.As for IP Logger, I don't recommend using it when trying to track down professionals. This program is more like a child's toy, rather than a working tool, and a more or less advanced user will immediately suspect something bad.

Fingerprinting
Since sites on Tor are not prohibited from using all standard technologies, fingerprinting can also work here — tracking users through unique fingerprints.For an example, let's look at the site AmIUnique.org. The service will easily detect the engine version, OS, language, fonts, plugins, and with some accuracy — the audio and video plugins supported by the browser. It's hard to call this an accurate identification, but identifying one suspect out of a thousand might help.
Tor Browser specially masks the screen resolution to make identification more difficult, plus users can replace the fingerprint themselves based on the canvas tag. All this makes fingerprinting less accurate, but it doesn't prevent it completely.

There are also more sophisticated tactics based on fingerprinting. Not everyone knows that if you open Tor Browser and normal and then switch between them with hot keys or the mouse, you can get a link between your real IP and the IP in the Tor network. They bring up unique patterns like the position of the mouse cursor, which can be tracked. The same goes for using two tabs in Tor Browser. Tor will use different input nodes for them, but if JavaScript is enabled, the relationship between tabs can still be established.

Text analysis
It's no secret that everyone has their own style of social media posts, and forum and marketplace administrators are no exception. Someone often puts spaces before commas, someone is not a fan of uppercase letters, and someone just has a broken keyboard and some button is often not pressed.All these little features will help you find other accounts on other forums, social networks, and so on. It is said that such mistakes were made by Ross Ulbricht, the owner of a large marketplace Silk Road.
Crawlers, spiders, and scrapers
There are different types of tools for collecting data on the Internet.- Crawler is a program that automatically crawls websites and collects information. It works like spiders, but it can collect different types of information.
- Scraper — a program that extracts data from websites, often automatically, and saves it in a structured format for further processing.use or analysis.
- Spider is a program that automatically follows links on websites, analyzes the content of pages, and indexes them for search or other purposes.
Let's start with crawlers. They can be used to collect a certain type of data on a site, such as photos, videos, text, and so on. For example, you want to go through all the photos on your site and find those that contain metadata.
Here are some Onion crawlers:
Scrapers work according to a predefined algorithm that determines what data to collect and how to extract it. They usually make requests to the server, and then analyze the resulting HTML to extract the necessary information. Various methods of parsing pages are used: HTML parsing, search by tags and CSS classes, regular expressions, and so on. Often sites are uploaded in their entirety for further analysis.
Here are some scraping programs and libraries:
Spiders are designed to index hundreds or thousands of links. For Tor, there are Onioff и Onion Spider.

Forensic science
In the end, we will touch on the topic of forensic science, not OSINT. When performing a forensic technical examination of a computer that used Tor, you should first check the following information::- Папку C:\Windows\Prefetchwhere files related to the launch of Tor Browser can be located (the executable file of the browser or DLL files loaded during its operation). Analyzing their timestamps allows you to determine when the browser was launched.
- Thumbnail cache. It can store previews of images viewed through Tor. They can be mapped to specific sites.
- The paging file. Here, too, you can find information about launching the browser, visiting sites, and file operations related to using Tor.
- The Windows registry. It helps you extract browser settings, session history, cached data, and records of downloaded extensions and plugins.
You can use the Regshot program to analyze the registry.
For network traffic analysis, I recommend Wireshark and NetworkMiner. Wireshark is good for detecting different types of packets and establishing connections between nodes. It helps you identify the characteristics of the protocols used in Tor. And NetworkMiner specializes in analyzing network traffic and identifying hidden connections and patterns. NetworkMiner can help you detect and analyze Tor network activity, including sharing information and using anonymous proxy servers.
And of course, you need to study the database of the Tor Browser itself. It is located along this path:
TorBrowser\Browser\TorBrowser\Data\Browser\Profile.default
Here, with certain browser settings, you can store your browsing history, bookmarks, saved passwords, cookies, and other user data.
Studying the data of Bitcoin wallets is a separate and complex topic, but you can use the Internet Evidence Finder to collect evidence.

