Brother
Professional
- Messages
- 2,590
- Reaction score
- 533
- Points
- 113
When will IT giants finally fix a fundamental flaw in their advertising services?
Recently, security experts from Malwarebytes identified a malicious campaign aimed at Chinese-speaking users who became victims of intruders thanks to the Google Ads advertising service.
Cybercriminals used Google advertisers accounts to create fraudulent ads that redirect users to web pages that download the Remote Access Trojan (RAT). The program allows attackers to fully control the victim's computer and install any additional malicious applications.
The campaign, codenamed FakeApp, is a continuation of attacks launched in October 2023 against users in Hong Kong who tried to download messaging apps such as WhatsApp and Telegram.
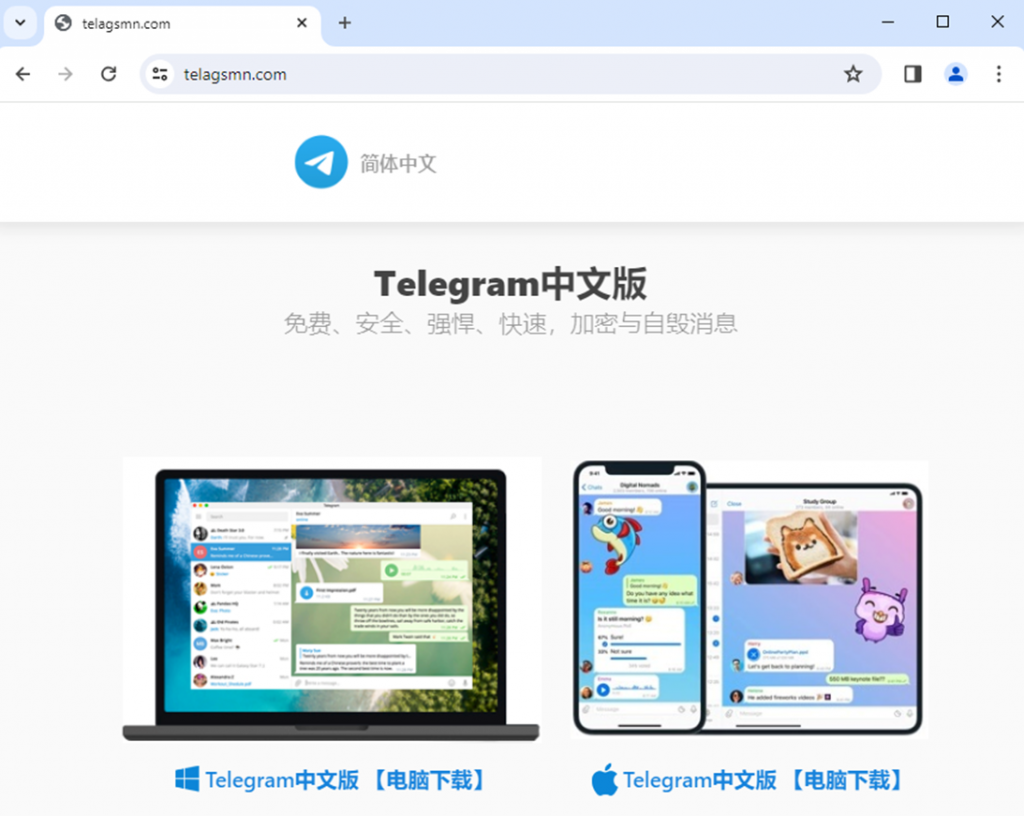
Phishing page for downloading Telegram, promoted through Google Ads
During the attack, users are redirected to fake sites hosted on the Google Docs and Google Sites platforms. Google's infrastructure is used to embed links to sites controlled by malicious users to download Trojan installers such as PlugX and Gh0st RAT.
In the new version of the campaign, the target audience is expanded by adding a new bait-another popular messenger called LINE.
Malwarebytes traced the fraudulent ads to two advertiser accounts: Interactive Communication Team Limited and Ringier Media Nigeria Limited, both based in Nigeria. It is noted that cyber villains prefer quantity to quality, constantly updating both the list of malicious programs and expanding their infrastructure.
In general, the Google Ads advertising service likes to be exploited by hackers all over the world. So, recently we wrote about how Google sponsored ads are used by hackers to distribute free software for Windows, which is deliberately embedded with malicious code.
To avoid becoming a victim of similar attacks, you need to be more careful on the web: check links, files, and applications before downloading, and use antivirus software.
Recently, security experts from Malwarebytes identified a malicious campaign aimed at Chinese-speaking users who became victims of intruders thanks to the Google Ads advertising service.
Cybercriminals used Google advertisers accounts to create fraudulent ads that redirect users to web pages that download the Remote Access Trojan (RAT). The program allows attackers to fully control the victim's computer and install any additional malicious applications.
The campaign, codenamed FakeApp, is a continuation of attacks launched in October 2023 against users in Hong Kong who tried to download messaging apps such as WhatsApp and Telegram.

Phishing page for downloading Telegram, promoted through Google Ads
During the attack, users are redirected to fake sites hosted on the Google Docs and Google Sites platforms. Google's infrastructure is used to embed links to sites controlled by malicious users to download Trojan installers such as PlugX and Gh0st RAT.
In the new version of the campaign, the target audience is expanded by adding a new bait-another popular messenger called LINE.
Malwarebytes traced the fraudulent ads to two advertiser accounts: Interactive Communication Team Limited and Ringier Media Nigeria Limited, both based in Nigeria. It is noted that cyber villains prefer quantity to quality, constantly updating both the list of malicious programs and expanding their infrastructure.
In general, the Google Ads advertising service likes to be exploited by hackers all over the world. So, recently we wrote about how Google sponsored ads are used by hackers to distribute free software for Windows, which is deliberately embedded with malicious code.
To avoid becoming a victim of similar attacks, you need to be more careful on the web: check links, files, and applications before downloading, and use antivirus software.

