Brother
Professional
- Messages
- 2,590
- Reaction score
- 533
- Points
- 113
Overview of the key findings of the Kaspersky Lab report.
The spread of malware is still an urgent threat to cybersecurity. Attackers use various types of ransomware programs that steal or encrypt data to get a ransom. Below are the main findings from Kaspersky Lab's report on three key threats: the FakeSG campaign, the Akira cryptographer, and the AMOS styler.
FakeSG Campaign
FakeSG is a new NetSupport RAT distribution campaign, named after the well-known SocGholish campaign. The attackers ' method is to infect legitimate sites, which then offer visitors to update their browser, leading to the download of a malicious file. To mask the activity, the domains from which the download takes place change regularly, but the path inside the domain remains unchanged (/cdn/wds.min.php).
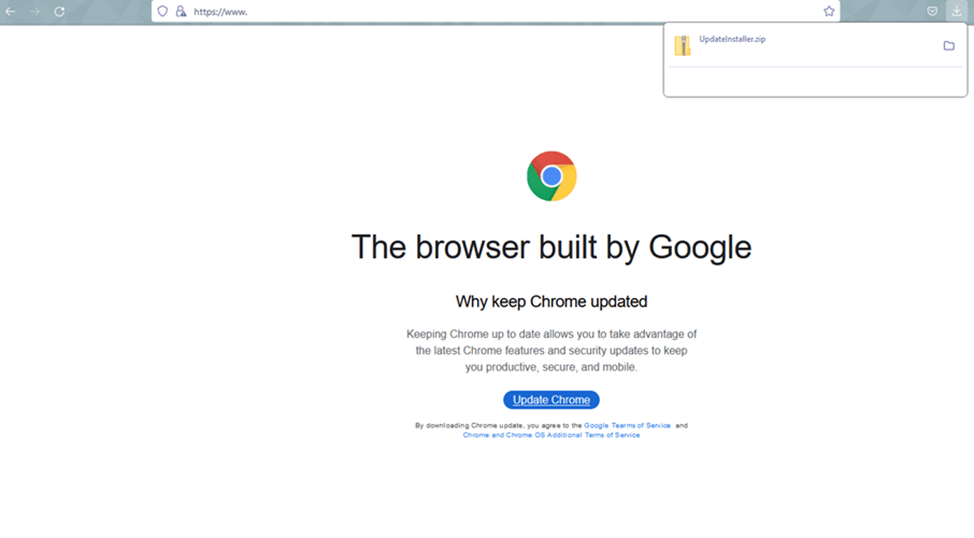
Landing page example
The uploaded file contains obfuscated JavaScript code. When executed, it downloads another script from the remote storage and sets a cookie. Then it displays a notification about the need to update the browser and starts automatically downloading the third script. This time we are talking about a batch file that loads another batch file, an archive in 7z format, and an executable file of the 7z archiver.
The second batch file is responsible for pinning it to the system by creating a task named VCC_runner2 in the scheduler, extracting and copying malware, and other tasks. Part of the contents of the 7z archive is a malware configuration file containing the address of the command server.
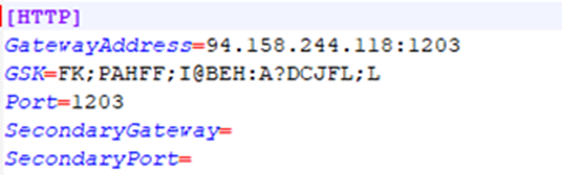
Address of the command server
Akira Cryptographer
Akira, discovered in April of this year – is a cryptographer for Windows and Linux operating systems. It is written in C++. Despite its relative novelty, Akira has already reached more than 60 organizations worldwide. They target large organizations in various industries, such as retail, consumer goods, and education. This tool works on the principle of classic cryptographers: it removes shadow copies and encrypts the contents of logical disks, skipping certain types of files and directories, while the stolen data is placed on a site on the Tor network, which is also used to communicate with intruders.
Interestingly, Akira has similarities with the Conti cryptographer. For example, the list of folders excluded from the encryption process is the same. It includes, in particular, the winnt folder, which is present only in Windows 2000. In addition, both cryptographers use similar string obfuscation functions. The Akira site, designed to communicate with intruders, is different from the rest. It was created in a minimalistic retro style using the jQuery Terminal library. The developers have taken a number of measures to protect it. For example, if you try to open the site using the debugger in the browser, an error occurs.
AMOS Stealer
AMOS, which entered the market in April 2023, quickly gained popularity among cybercriminals. This stealer for macOS, originally written in Go, now uses the C language. An ad in Telegram offered cybercriminals to use it for $ 1,000 a month. Infection methods include spreading through malicious advertising and fake sites, namely: attackers clone sites with popular software and lure users there by tricking them into downloading a malicious DMG file. When you open it, you will see instructions for installing malware disguised as legitimate software:
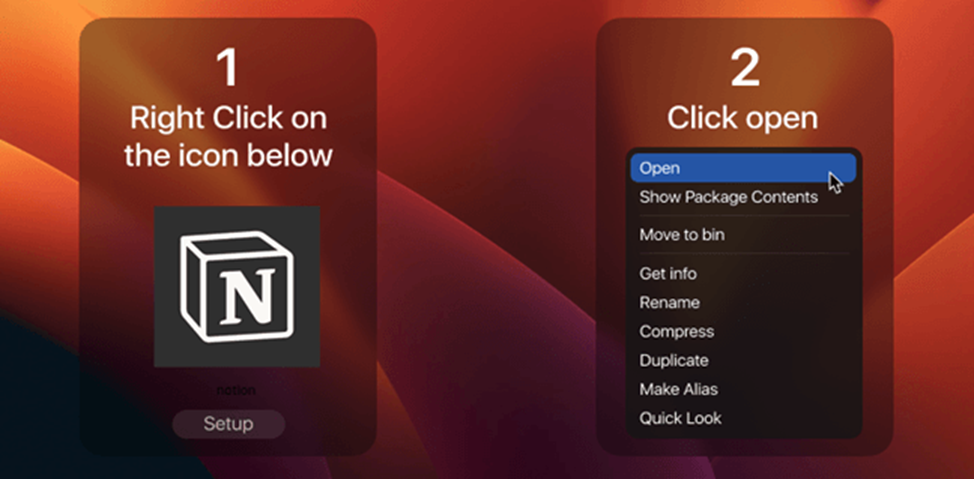
Instructions for installing malware
First of all, the malware gets the user's name and checks whether it needs a password to log in, and if so, whether this password is empty. If the password is required and not empty, but the user is not logged in, a pop-up window is created using osascript asking for the password.
AMOS is capable of stealing various user data, including information from browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, and messenger data. Data is packaged using the miniz library and sent to the command server over the HTTP protocol. Part of the request is a UUID that identifies the campaign or malware buyer. AMOS infections have been reported all over the world, especially in Russia and Brazil.
The spread of malware is still an urgent threat to cybersecurity. Attackers use various types of ransomware programs that steal or encrypt data to get a ransom. Below are the main findings from Kaspersky Lab's report on three key threats: the FakeSG campaign, the Akira cryptographer, and the AMOS styler.
FakeSG Campaign
FakeSG is a new NetSupport RAT distribution campaign, named after the well-known SocGholish campaign. The attackers ' method is to infect legitimate sites, which then offer visitors to update their browser, leading to the download of a malicious file. To mask the activity, the domains from which the download takes place change regularly, but the path inside the domain remains unchanged (/cdn/wds.min.php).

Landing page example
The uploaded file contains obfuscated JavaScript code. When executed, it downloads another script from the remote storage and sets a cookie. Then it displays a notification about the need to update the browser and starts automatically downloading the third script. This time we are talking about a batch file that loads another batch file, an archive in 7z format, and an executable file of the 7z archiver.
The second batch file is responsible for pinning it to the system by creating a task named VCC_runner2 in the scheduler, extracting and copying malware, and other tasks. Part of the contents of the 7z archive is a malware configuration file containing the address of the command server.

Address of the command server
Akira Cryptographer
Akira, discovered in April of this year – is a cryptographer for Windows and Linux operating systems. It is written in C++. Despite its relative novelty, Akira has already reached more than 60 organizations worldwide. They target large organizations in various industries, such as retail, consumer goods, and education. This tool works on the principle of classic cryptographers: it removes shadow copies and encrypts the contents of logical disks, skipping certain types of files and directories, while the stolen data is placed on a site on the Tor network, which is also used to communicate with intruders.
Interestingly, Akira has similarities with the Conti cryptographer. For example, the list of folders excluded from the encryption process is the same. It includes, in particular, the winnt folder, which is present only in Windows 2000. In addition, both cryptographers use similar string obfuscation functions. The Akira site, designed to communicate with intruders, is different from the rest. It was created in a minimalistic retro style using the jQuery Terminal library. The developers have taken a number of measures to protect it. For example, if you try to open the site using the debugger in the browser, an error occurs.
AMOS Stealer
AMOS, which entered the market in April 2023, quickly gained popularity among cybercriminals. This stealer for macOS, originally written in Go, now uses the C language. An ad in Telegram offered cybercriminals to use it for $ 1,000 a month. Infection methods include spreading through malicious advertising and fake sites, namely: attackers clone sites with popular software and lure users there by tricking them into downloading a malicious DMG file. When you open it, you will see instructions for installing malware disguised as legitimate software:

Instructions for installing malware
First of all, the malware gets the user's name and checks whether it needs a password to log in, and if so, whether this password is empty. If the password is required and not empty, but the user is not logged in, a pop-up window is created using osascript asking for the password.
AMOS is capable of stealing various user data, including information from browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, and messenger data. Data is packaged using the miniz library and sent to the command server over the HTTP protocol. Part of the request is a UUID that identifies the campaign or malware buyer. AMOS infections have been reported all over the world, especially in Russia and Brazil.

